Insights:
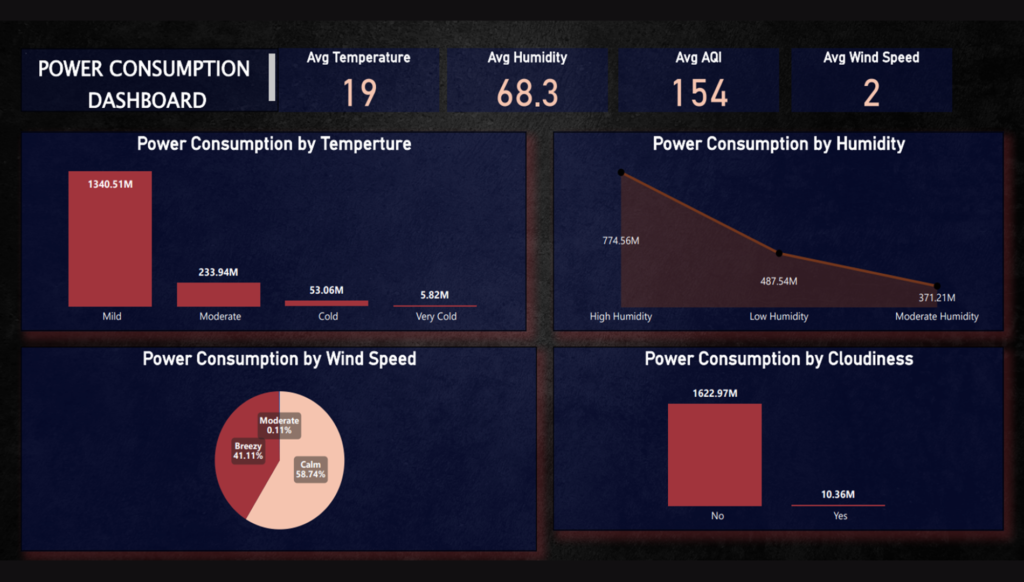
Temperature and Power Consumption: There is a direct and logical relationship between temperature and power consumption. As temperatures rise, power consumption tends to increase. This is a common phenomenon as people use air conditioning, cooling systems, and other appliances more frequently in hot weather.
Cloudy Weather and Reduced Power Consumption: Power consumption tends to decrease during cloudy weather. This suggests that when the weather is overcast, people may use less energy for heating or cooling their homes, resulting in lower overall power consumption.
High Humidity and Power Consumption: High humidity levels are associated with increased power consumption. This could be due to the use of dehumidifiers, air conditioning systems, or fans to maintain comfort levels in humid conditions.
Profitability in High-Temperature and High-Humidity Regions: The dashboard indicates that the region is experiencing both high temperatures and humidity levels. This suggests that the power company operating in this region may see higher profitability during these conditions due to increased power demand.
Recommendations:
Capacity Planning: Based on the insights regarding temperature and humidity, the power company should conduct thorough capacity planning. Ensure that the power generation and distribution infrastructure can handle the increased demand during periods of high temperature and humidity. This includes maintaining and upgrading equipment as needed.
Energy Efficiency Programs: Implement energy efficiency programs that educate customers on ways to reduce power consumption during hot and humid weather. Encourage the use of energy-efficient appliances, proper insulation, and smart thermostats to optimize energy usage.
Weather-Based Pricing: Consider implementing dynamic pricing models that take into account weather conditions. Offer lower rates during off-peak hours or cooler weather to incentivize energy consumption when demand is lower.
Renewable Energy Integration: Explore opportunities for integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, into the energy mix. Renewable sources can help meet increased demand during peak periods and reduce the environmental impact.
Grid Modernization: Invest in grid modernization to enhance grid reliability and flexibility. This includes the deployment of smart grid technologies, which can better balance supply and demand during extreme weather conditions.
Customer Engagement: Engage with customers to promote energy conservation practices during hot and humid weather. Provide tips, educational materials, and incentives to encourage responsible energy use.
Data Analytics: Continuously analyze data on temperature, humidity, and power consumption to refine predictive models. This can help the power company anticipate demand patterns and make proactive adjustments to meet customer needs.
Environmental Considerations: In regions with high power consumption during extreme weather conditions, consider the environmental impact. Explore ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability in power generation.